What’s The Difference Between Good And Bad Calories?

A creative writer with a voracious appetite for fashion, beauty,…
T
he word “calorie” has become synonymous with diets, weight loss, and the pursuit of a perfect physique. We meticulously count and restrict our calorie intake, believing that this numerical value holds the key to our health and well-being. But what if there is a deeper story behind calories, one that extends far beyond weight loss? What if the quality of calories we consume plays a vital role in our health and vitality? What if there are good calories our bodies need to survive?
Understanding good and bad calories
Beyond their energy content, calories carry a unique power to shape our health and vitality. Some calories offer essential nutrients, while others provide empty, fleeting energy that leaves us feeling unsatisfied. By understanding the distinction between good and bad calories, we can make informed choices that nourish our bodies and optimize our overall wellness.
Calories can be understood as a measure of energy contained in the food we eat. Think of calories as the fuel that powers our bodies to function properly. Just like a car needs fuel to run, our bodies need calories to carry out everyday activities like walking, breathing, and even thinking. This brings us to the good and bad calories.
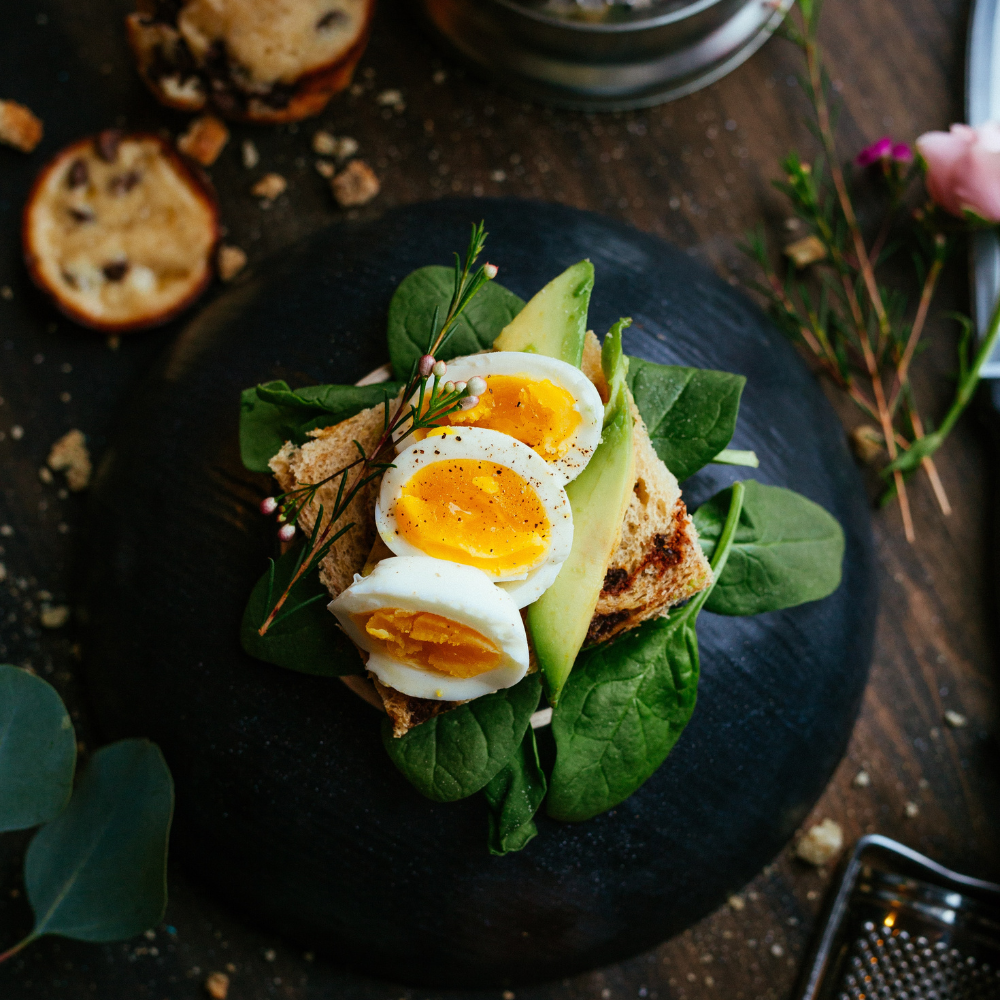
What are good calories?

Good calories refer to those derived from nutrient-dense foods that provide diverse essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, fiber, and healthy fats. These calories are often found in whole, unprocessed foods and contribute to overall health and well-being. Some key characteristics of good calories are:
- Nutrient density: Good calories are rich in nutrients relative to their calorie content. They provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support optimal bodily functions and promote general health.
- Satiety: Good calories tend to be more filling and satisfying due to their higher fiber and protein content. They help regulate appetite, reduce cravings, and provide a sustained release of energy.
- Health benefits: Consuming good calories is associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. They support a healthy metabolism, and immune function, and promote optimal organ functioning.
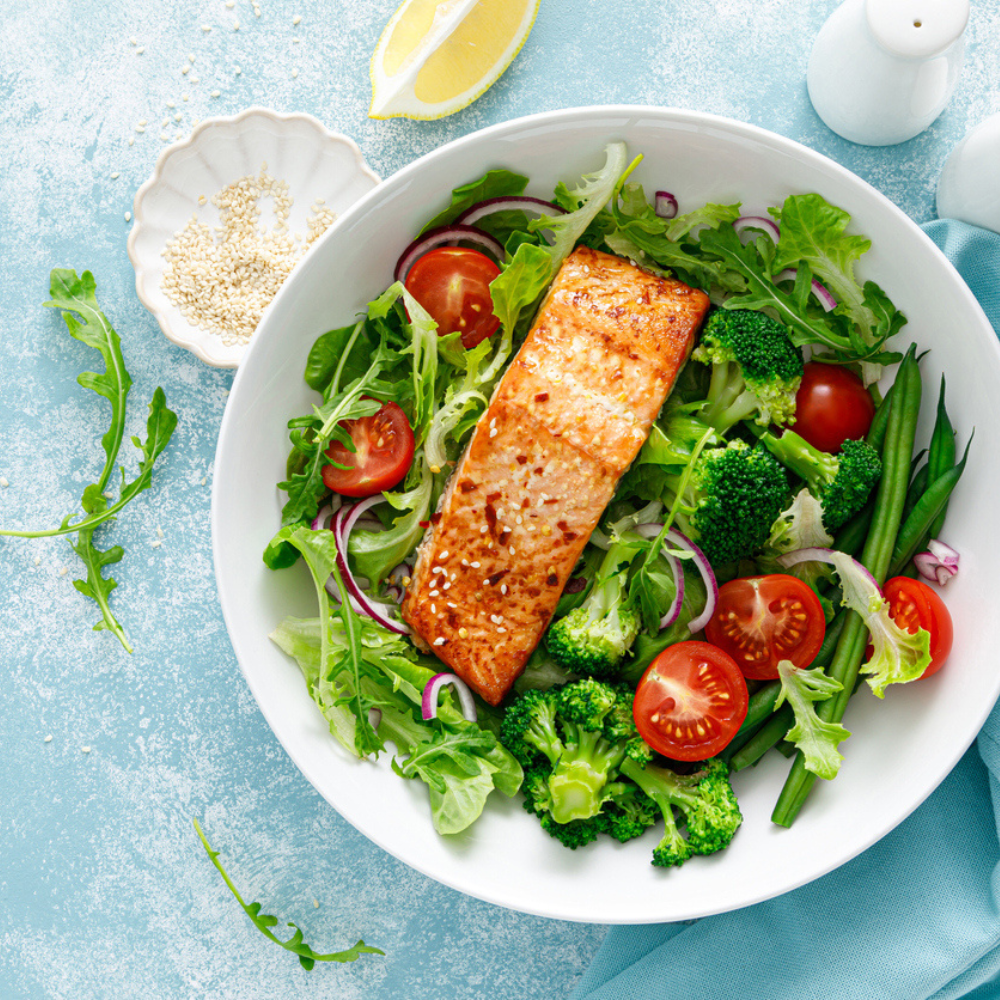
Examples of foods with good calories include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
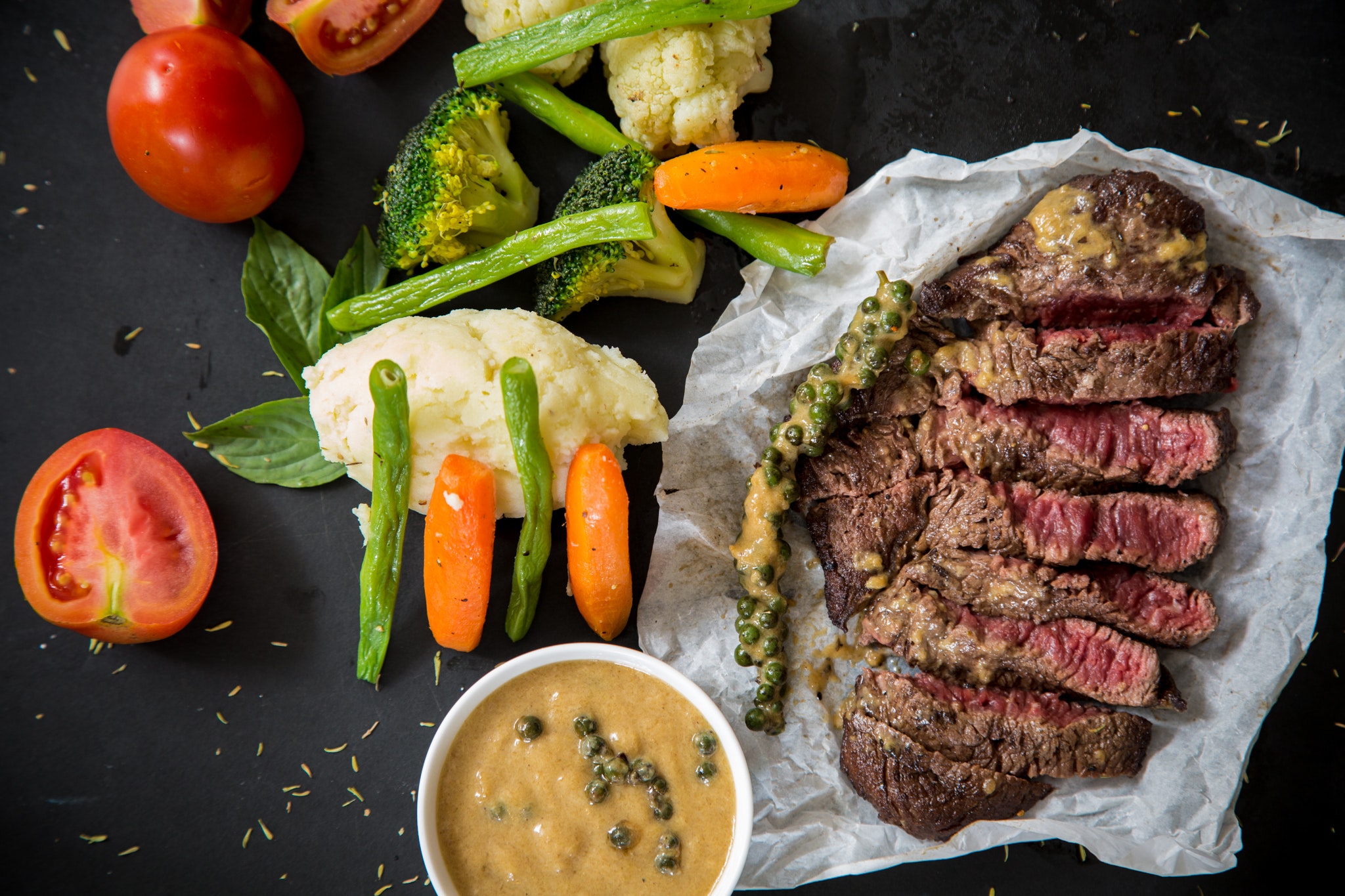
What are bad calories?
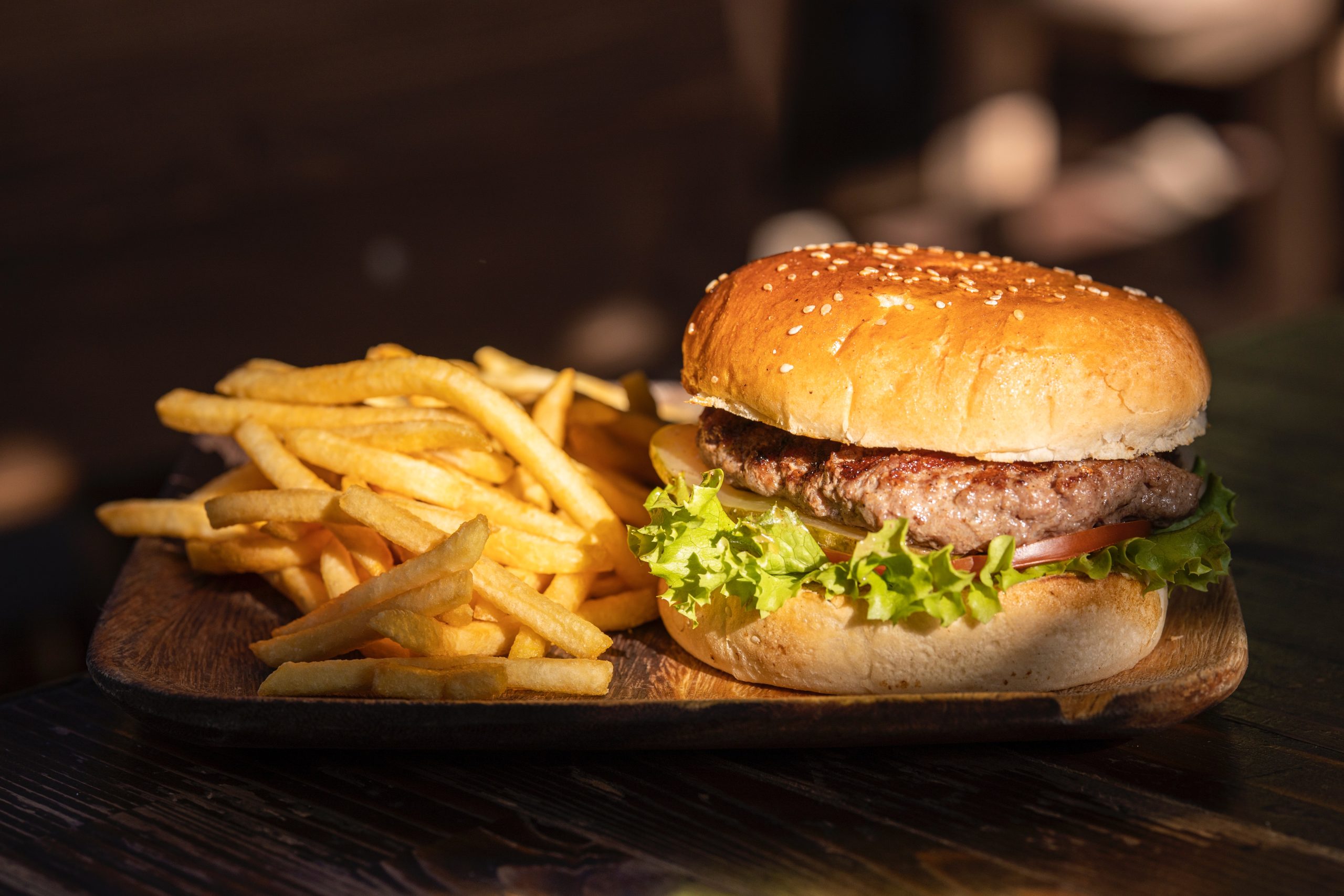

Bad calories, on the other hand, refer to those derived from highly processed, nutrient-poor foods high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives. These calories offer little to no nutritional value and can have detrimental effects on health. Some key characteristics of bad calories are as follows:
- Nutrient-poor: Bad calories lack essential nutrients and are often referred to as “empty calories.” They provide excessive amounts of sugar, unhealthy fats, and refined carbohydrates without significant nutritional benefits.
- Low satiety: Bad calories are typically low in fiber and protein, which can lead to quick spikes in blood sugar levels followed by crashes. This can lead to feelings of hunger and contribute to overeating and weight gain.
- Health risks: Consuming a diet high in bad calories has been linked to an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and other chronic conditions. These calories often contribute to weight gain and can negatively impact overall well-being.
Examples of foods with bad calories include sugary beverages, processed snacks, fast food, desserts, fried foods, and refined grains.
Strategic ways to avoid bad calories

Here are some strategies to help you avoid bad calories and choose good calories:
- Fill your plate with real, whole foods: When it comes to making better food choices, think about filling your plate with real foods that come straight from nature. Fresh fruits, lush vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and nourishing nuts and seeds are all great options. These foods are loaded with nutrients, and offer a wide range of health benefits.
- Watch out for sneaky added sugars: Be cautious of foods and drinks that sneakily hide added sugars. They can be found in sodas, sugary snacks, and even seemingly innocent items like flavored yogurts or granola bars. Instead, satisfy your sweet tooth with naturally sweet fruits or opt for products with no added sugars.
- Become a savvy label reader: To know the difference between good and bad calories, knowledge is power. Take a moment to read food labels and become aware of what’s really in your food. Check the ingredient list for added sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives. Choose products with simple, recognizable ingredients and keep an eye out for hidden culprits.
- Embrace the goodness of healthy fats: Don’t shy away from healthy fats. Foods like avocados, nuts, and fatty fish are rich in beneficial fats that support your body’s needs. These fats can help keep you feeling satisfied and provide essential nutrients.
- Pile on the protein: Always include sources of lean protein in your meals. Skinless poultry, fish, legumes, and tofu are all fantastic choices. Protein not only helps with muscle repair and growth but also helps keep you feeling full and satisfied.
- Fiber is your friend: Boost your fiber intake by incorporating fiber-rich foods into your meals. Whole grains, fresh fruits, vegetables, and legumes are all excellent sources. Fiber helps digestion and helps you feel fuller for longer, which can prevent overeating.
- Become the chef of your kitchen: Take control of your meals by cooking at home. When you prepare your own meals, you have complete control over the ingredients and cooking methods. Experiment with fresh ingredients, herbs, and spices to create flavorful and wholesome dishes.
- Choose healthier cooking techniques: Opt for healthier cooking methods like baking, grilling, steaming, or sautéing. These techniques require less added fats and oils compared to deep-frying or pan-frying, which can add unnecessary calories.
- Stay hydrated with the ultimate quencher: Quench your thirst with nature’s best hydrator—water. It’s calorie-free, refreshing, and essential for your body’s optimal functioning. Skip the sugary drinks and opt for water as your go-to beverage.
- Listen to your body’s signals: Pay attention to your body’s signals of hunger and fullness. Eat when you’re truly hungry, and stop when you feel satisfied. Practice mindful eating, savor your meals, and avoid distractions that may lead to mindless munching.
Featured image: Joseph Gonzalez/Unsplash
For the latest in fashion, lifestyle, and culture, follow us on Instagram @StyleRave_
This is a Style Rave original content exclusively created for our readers. If reproduced, distributed, transmitted, cached, or otherwise used by any other publishing house or blogs, such use should provide a direct link to this source article. Use of and/or registration on any portion of this site constitutes acceptance of our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy.
—Read also
A creative writer with a voracious appetite for fashion, beauty, lifestyle and culture. As one who's passionate about the advancement of the woman, creating content that inspire smart style and living, and positive lifestyle changes is a calling I take seriously. At Style Rave, we aim to inspire our readers by providing engaging content to not just entertain but to inform and empower you as you ASPIRE to become more stylish, live smarter and be healthier. Follow us on Instagram @StyleRave_ ♥